ERDC/CHL CHETN-I-69
March 2005
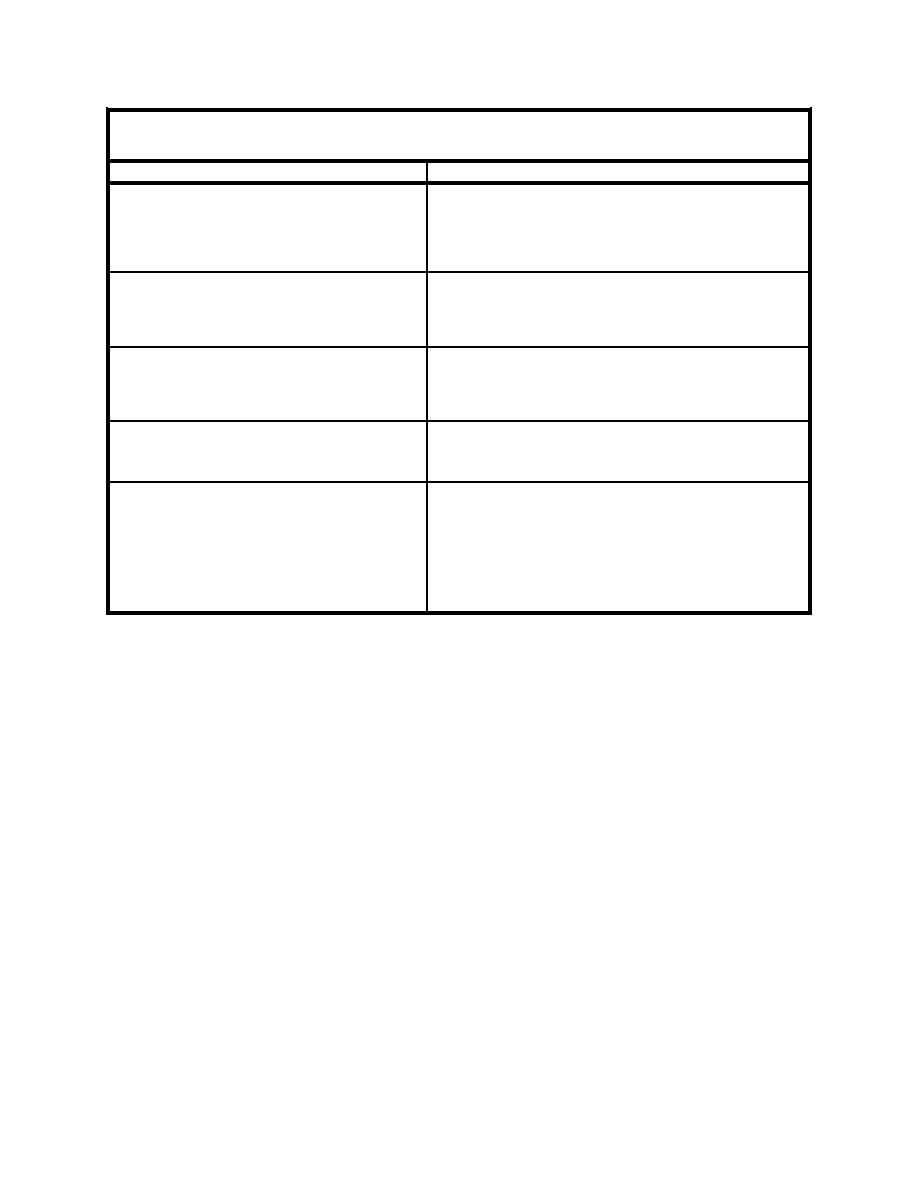
Table 5.
Irregular Unidirectional Wave Spectral Parameters
Method
Required Parameters
TMA spectrum (shallow water)
Significant wave height (Hs)
Peak wave period (Tp)
Gamma
Minimum wave period (Tmin)
Maximum wave period (Tmax)
Whether to rescale the spectrum or not
JONSWAP spectrum
Hs and Tp or wind speed and fetch distance
Gamma
Minimum wave period (Tmin)
Maximum wave period (Tmax)
Whether to rescale the spectrum or not
Bretschneider (ITTC) spectrum
Significant wave height (Hs)
Peak wave period (Tp)
Minimum wave period (Tmin)
Maximum wave period (Tmax)
Whether to rescale the spectrum or not
Pierson-Moskowitz spectrum
Wind speed or Hs or Tp
Minimum wave period (Tmin)
Maximum wave period (Tmax)
Whether to rescale the spectrum or not
Ochi-Hubble double peak spectrum
Hs for the low frequency
Tp for the low frequency
Tp for the high frequency
Gamma for the low frequency
Gamma for the high frequency
Minimum wave period (Tmin)
Maximum wave period (Tmax)
Whether to rescale the spectrum or not
(3) Irregular multidirectional waves. Irregular multidirectional waves can be generated in the
following ways:
By using an input water-surface elevation time series file (*.ts1). The user specifies
which *.ts1 file to use and the directional distribution function.
By using an input directional spectrum file (*.dws) either from field measurements or
generated in the spectral generator. The user specifies the range of frequencies and generates a
spectrum from observed data or from the output of another model such as STWAVE. Spectra may
also be generated from parameters for all of the types listed in Table 5. The spectral generator can be
used to visualize the spectra as well. Viewing options include both Cartesian and polar projection of
the spectral grid and allow selection of individual frequency, direction combinations to view the
energy component. The user can also rotate the spectra to examine or better understand the wave
conditions in a simulation.
From a parametric directional wave spectrum by specifying the spectral and directional
parameters. The user also has to specify the random number seed and time series duration. This is
similar to the unidirectional waves previously described, but adds directional spreading parameters.
The spreading parameters determine how the generated wave spectrum is spread directionally. Two
spreading options are available for irregular multidirectional waves. These are wrapped normal
distribution and cosine power function. With the wrapped normal distribution, the user must specify
a standard deviation and a maximum angle cutoff. With the cosine power function, the user must
14



 Previous Page
Previous Page
