ERDC/CHL CHETN-I-68
March 2004
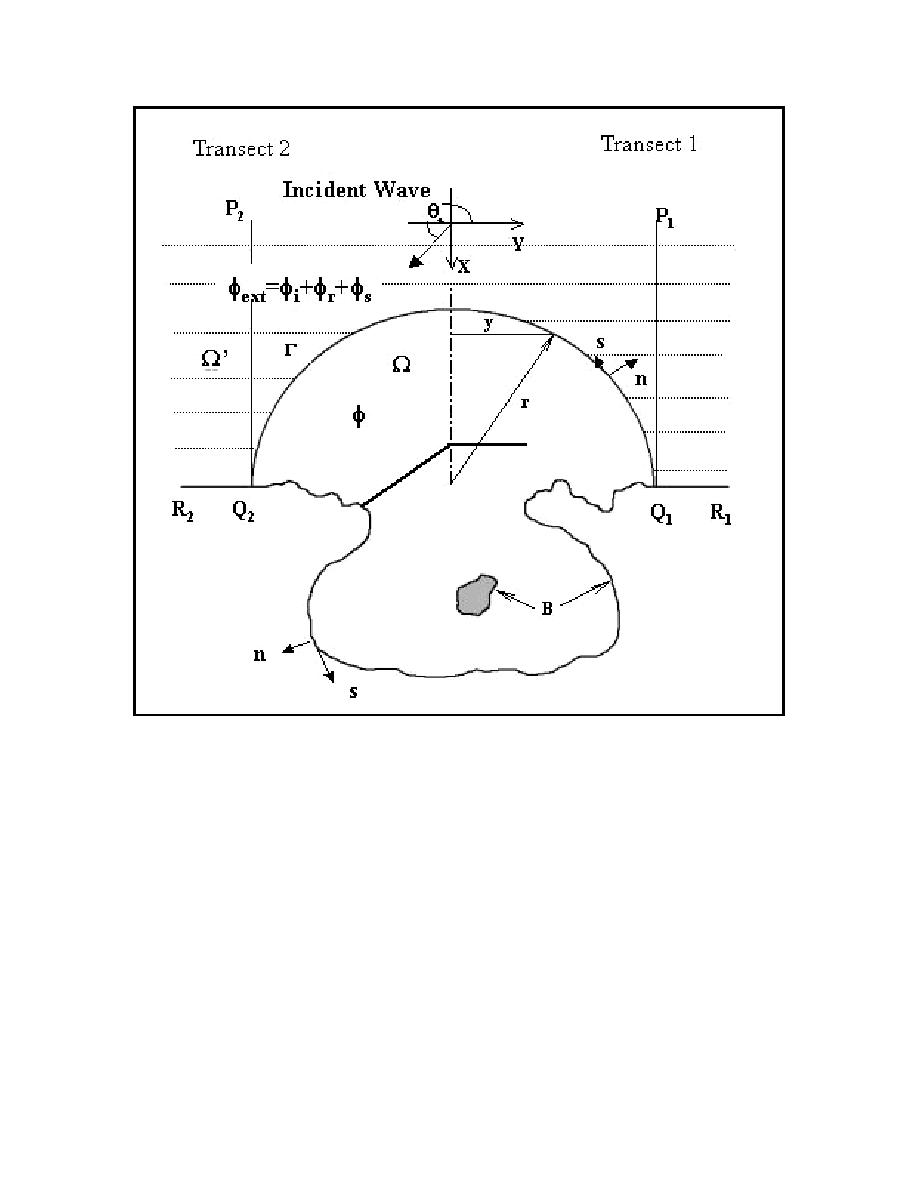
Figure 1.
Example of a CGWAVE model domain
CGWAVE accepts arbitrary domains (Figure 1) and structures using linear triangular finite elements.
The large number of discretized equations is solved with iterative and direct solvers as a steady state
problem. Convergence is guaranteed, but can be extremely slow on PC's with large model domains.
The ERDC High Performance Computing Center's (HPC) supercomputers can be used to quickly
solve large problems. Currently, the Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI) solver available on the SGI Origin
3000 supercomputer named "Ruby" provides reasonably fast run times with CGWAVE. The model
output is then transferred back to the PC for post-processing.
Both regular and spectral waves can be input. Spectral or irregular waves can be simulated by
combining regular wave cases. The wave direction is the direction the waves travel to and is
measured positive in a counterclockwise direction from east (i.e., 0 deg). Short and long waves,
including tsunamis, can be modeled.
2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
