ERDC/CHL CHETN-I-67
June 2003
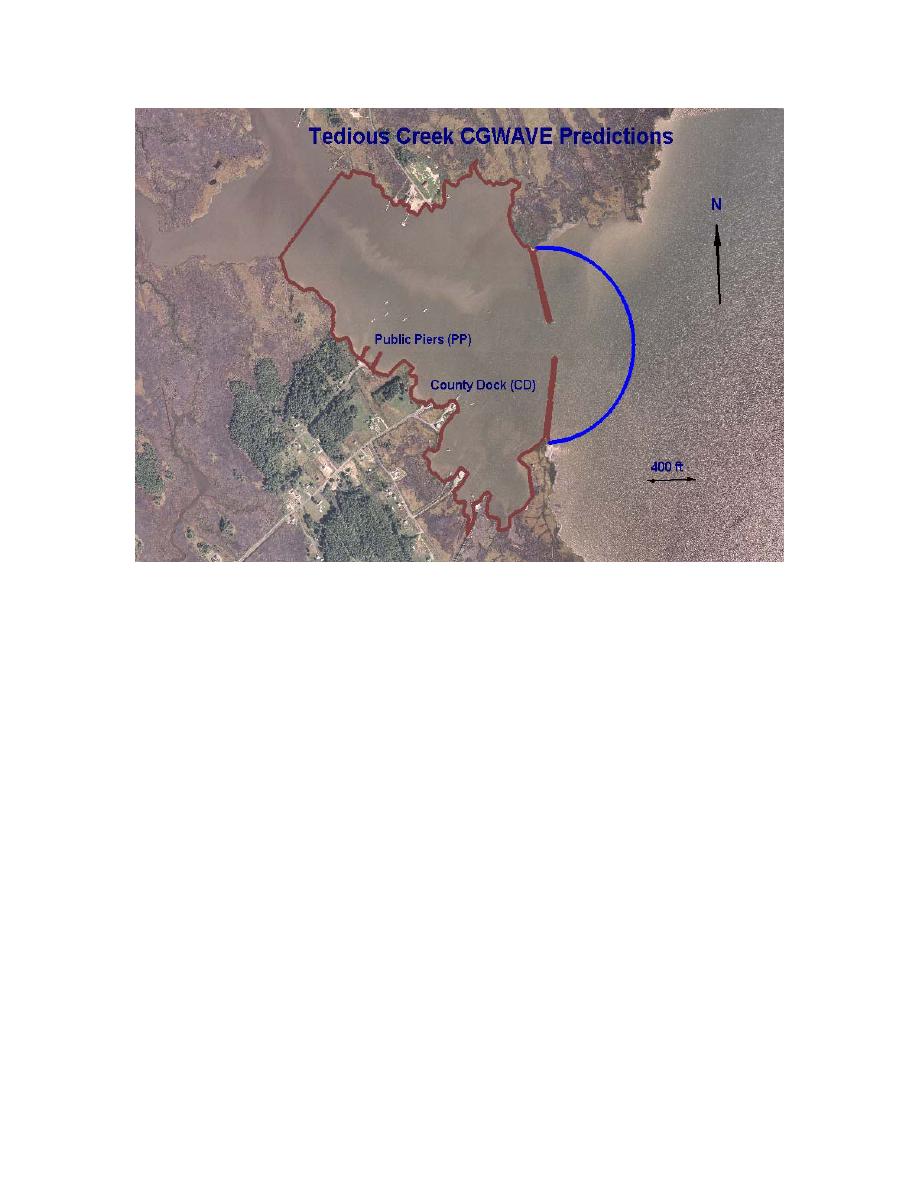
Figure 2. CGWAVE model for Tedious Creek, MD, with existing as-built gap of 122 m (400 ft)
6 sec are prevalent, the required grid size was 1.9 m (6.1 ft). Therefore, it was decided to limit the
model size to cover only the most critical areas inside and outside the harbor. The area within the
brown boundaries is more than adequate to model the wave conditions inside the harbor.
Bathymetric data were collected by CHL in August 2001 to provide an accurate baseline grid for the
modeled area inside and offshore of the breakwaters. The entire Tedious Creek estuary is shallow,
with depths less than 2.7 m (8.9 ft). The area outside the ocean boundary was not surveyed, but was
represented by contours from bathymetric charts of the area. These bathymetric contours were used
to model the one-dimensional (1-D) bathymetric lines offshore of the breakwaters required by
CGWAVE. Figure 3 shows a contour plot of water depth for a representative storm water level of
1.0 m (3.3 ft) mllw in the existing configuration.
Mean and spring tides range from 0.7 m (2.4 ft) to 0.9 m (3.0 ft), respectively. The 5-year water
level, including tide and storm effects, is 1.1 m (3.7 ft) above mllw (TC Report 1995). Thus, a water
level of 1.0 m (3.3 ft) mllw was selected as a representative worst case of normally occurring tide
and storm levels at Tedious Creek. Since storm wave heights are directly related to water level at
this shallow site, only the 1.0-m (3.3-ft) water level was modeled.
Two different model grids were created in CGWAVE. The existing as-built model included a
breakwater gap of 122 m (400 ft). The authorized project model has a breakwater gap of 91 m
(300 ft).
3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
