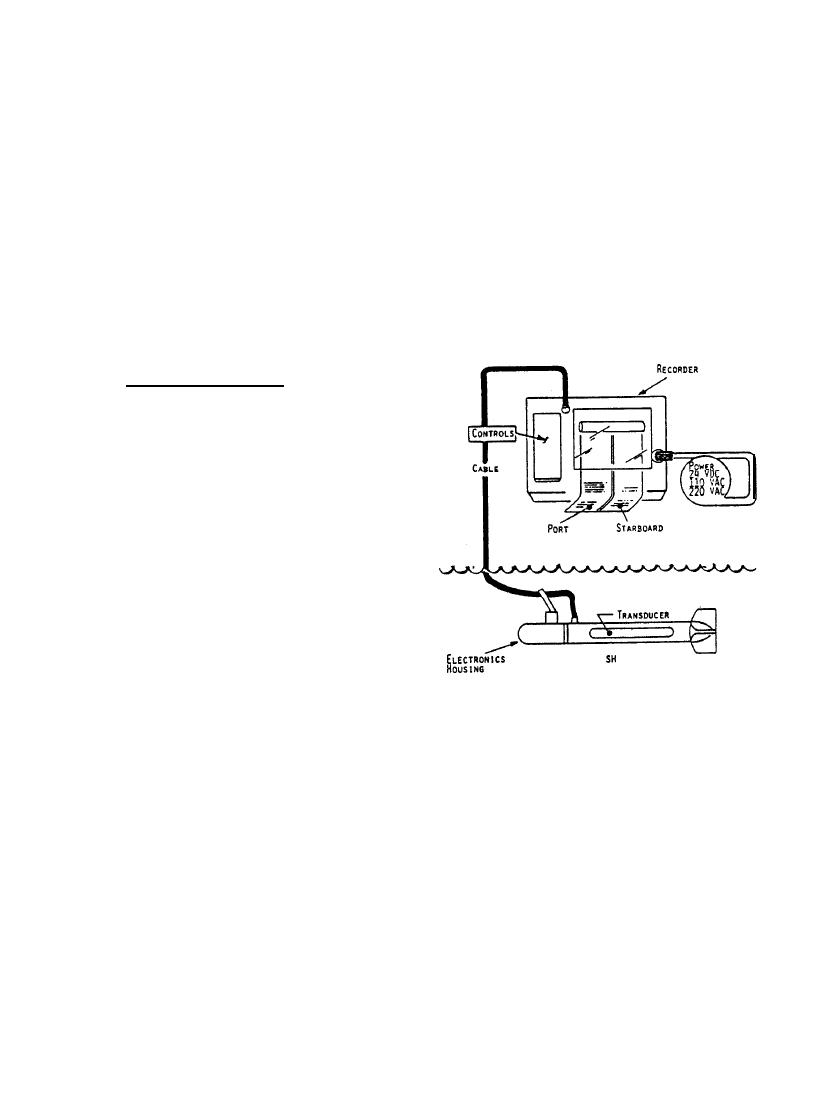
A typical SSS system consists of a pair of transducers mounted in a
c y l i n d r i c a l body or "towfish" and a dual channel recorder connected by a con-
T h e recorder's control section triggers the signal
ducting
cable
(Figure
2).
s e n t by the "towfish."
After a length of time determined by the-distance the
sound must travel, the signal is received and is printed as a darkened area by
t h e recorder.
Most SSS systems manufactured today operate at one of two fre-
quencies,
100 kilohertz (kHz) or 500 kHz.
The l00-kHz system normally is
used for locating objects and mapping the seafloor because the lower frequency
travels farther in water, covering a larger area.. The 500-kHz
system should
be used for inspecting underwater structures since the higher frequency sound
w a v e s allow better resolution of detail.
INSPECTION METHODS: Normally,
inspection
of
structures
with
SSS
is
done from a boat.
Inspections
should
not be attempted where waves are higher
than about 2 feet because the wave
motion is transmitted to the "fish," pro-
d u c i n g a smeared image. If wave heights
are no greater than a foot, boats from
16 to 25 feet long are stable enough to
operate
effectively.
However,
larger
boats are needed when waves are higher,
TOWF
I
and boats from about 40 to 50 feet long
Figure 2.
Typical Side Scan
would be required if waves were near
Sonar System
2 feet high.
( C o u r t e s y of Klein Assoc., Inc.)
The towfish
can be connected to
the boat's bow or amidships; however, towing from amidships works better.
L e s s of the boat's pitching motion will be transferred to the fish, and the
p o s i t i o n of the fish in the water can be more accurately controlled. Towing
the fish over the stern is not recommended because the cable can get tangled
i n the propeller.
A positioning system accurate to within a few feet is required to ac-
Positioning
curately locate the features recorded on a SSS printout sheet.
can be taken from horizcrtal control marks at regular intervals, about
The marks need to be visible from the
1 0 0 feet, along a coastal structure.
2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
